Most Plants Incorporate Carbon Dioxide Into Sugars By Means Of A Cycle Of Reactions Called The
This transforms the water into oxygen and the carbon dioxide into. The first is employed by plants called C3 plants most plants and it simply involves the pathway described above.

Arabidopsis Thaliana Vtc4 Encodes L Galactose 1 P Phosphatase A Plant Ascorbic Acid Biosynthetic Enzyme Journal Of Biological Chemistry Source: www.jbc.org
This is the only process in the cycle that decreases the level of.
Most plants incorporate carbon dioxide into sugars by means of a cycle of reactions called the. The plant cant eat so to get its energy like all life formes he as to produce it by him self. Asked Aug 24 2019 in Biology Microbiology by Redditor. Photosynthesis is the biochemical process that occurs in all green plants or autotrophs producing organic molecules from carbon dioxide CO2.
12Most plants incorporate carbon dioxide into sugars by means of a cycle of reactions called the ACAM cycle. 13Flattened sacs of internal membranes associated with photosynthesis are called Achloroplasts. The majority of plant species on Earth uses C3 photosynthesis in which the first carbon compound produced contains three carbon atoms.
Nearly all carbon dioxide fixation is accomplished by means of photosynthesis in which green plants form carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water using the energy of sunlight to drive the chemical reactions involved. Flattened sacs of internal membranes associated with photosynthesis are called. The process of incorporating carbon dioxide into the molecules of living matter is called fixation.
Most plants incorporate carbon dioxide into sugars by means of a cycle of reactions called the. Wheat oats rye orchardgrass are some of the examples of C3 plants. Light-dependent reactions As the name suggests it requires light and mainly.
Most plants incorporate carbon dioxide into sugars by means of a cycle of reactions called the. Energy for the reactions is supplied by ATP with NADPH see NADP acting as a reducing agent both having been produced in the light reactions of PHOTOSYNTHESIS. These plants carry out the C3 cycle to fix carbon from carbon dioxide into 3 carbon sugars.
One complete cycle incorporates three molecules of carbon dioxide and produces one molecule of the three-carbon compound glyceraldehyde-3. These organic molecules contain many carbon-hydrogen CH bonds and are highly reduced compared to CO2. There are two stages of Photosynthesis.
Professor Biochemistry and Biophysics at Oregon State University The Calvin Cycle is the means by which plants assimilate carbon dioxide from the atmosphere ultimately into glucose. In a process called Photosynthesis he uses water and carbon dioxide and with the help of the light energy from the sun usually transform them into suger called glucose a bay product is oxygen which we breeds. Green plants use carbohydrates to build the other organic molecules that make up their.
Almost all life forms use the TCA cycle to convert molecules such as amino acids sugars and lipids into energy and carbon dioxide by means of a. Within the plant cell the water is oxidized meaning it loses electrons while the carbon dioxide is reduced meaning it gains electrons. During photosynthesis plants take in carbon dioxide CO 2 and water H 2 O from the air and soil.
Photosynthesis captures energy from sunlight to convert carbon dioxide into carbohydrate. In this process carbon dioxide enters a plant through its stomata microscopic pores on plant leaves where amidst a series of complex reactions the enzyme Rubisco fixes carbon into sugar through the Calvin. A series of chemical reactions first described by Melvin CALVIN which take place in the watery matrix of CHLOROPLASTS where carbon dioxide is incorporated into more complex molecules and eventually carbohydrate.
The Calvin-Benson cycle in which carbon is fixed reduced and utilized involves the formation of intermediate sugar phosphates in a cyclic sequence. Photosynthesis plants absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and form it into sugar starch and other organic compounds. Carbon dioxide is converted into sugars in a process called carbon fixation.
Plants use two general strategies for doing so. The carbon-fixation pathway begins in the mesophyll cells where carbon dioxide is converted into bicarbonate which is then added to the three-carbon acid phosphoenolpyruvate PEP by an enzyme called phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase. When plants absorb carbon during whats known as the Calvin cycle the second stage of photosynthesis an enzyme called RuBisCO helps catalyse the reaction that turns CO2 into glucose which plants use as an energy source.
It is a cycle of chemical reactions where plants over a period of time can transform the 3 carbon compounds into nucleotides amino acids and complex sugars starches. Answered Aug 24 2019 by. Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that through cellular respiration can later be released to fuel the organisms metabolic activities.
This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules such as sugars and starches which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water hence the name photosynthesis from the Greek phōs. All this happenes in a special place called chloroplast which gives the plant its.
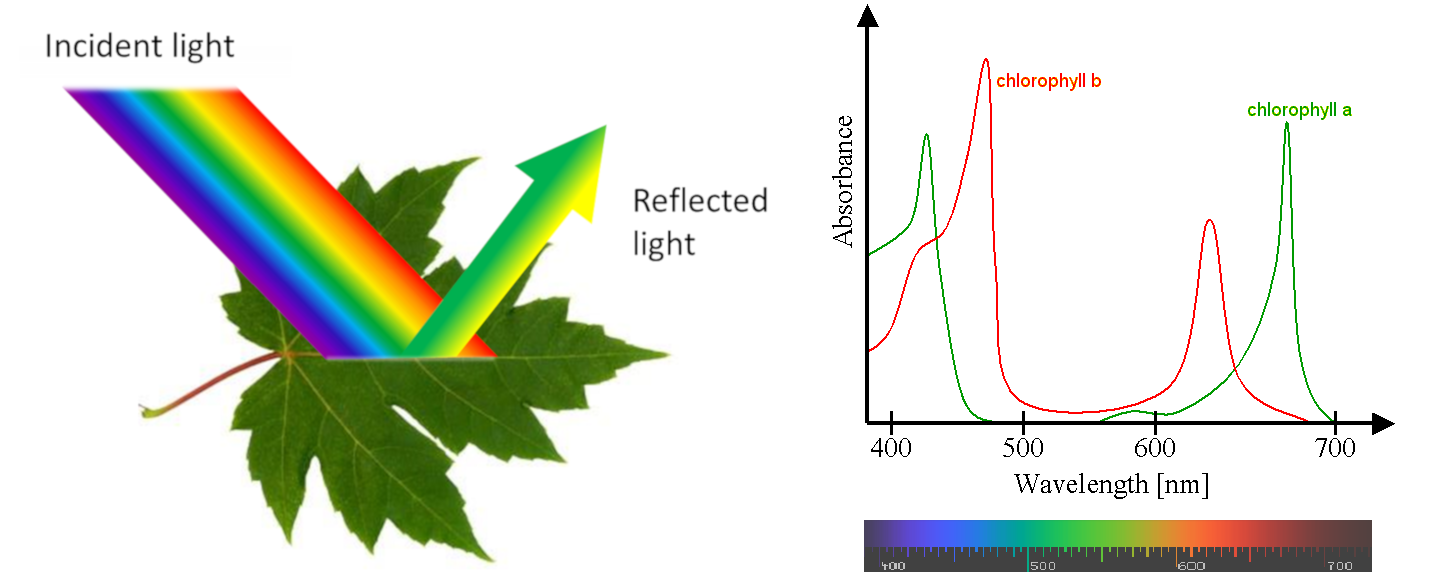
Shedding Light On Photosynthesis Encyclopedia Of The Environment Source: www.encyclopedie-environnement.org

Molecule Gallery Aromatic Rings Source: www.angelo.edu
The Calvin Cycle Article Photosynthesis Khan Academy Source: www.khanacademy.org
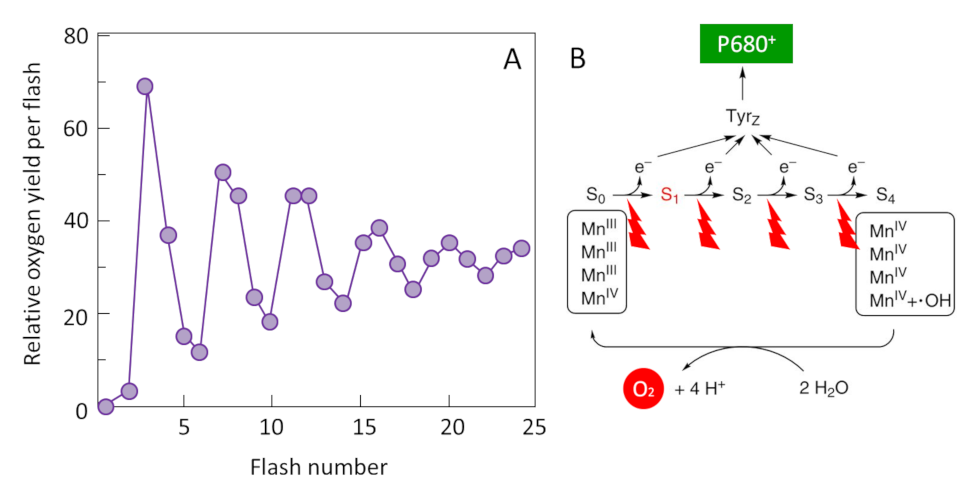
Shedding Light On Photosynthesis Encyclopedia Of The Environment Source: www.encyclopedie-environnement.org
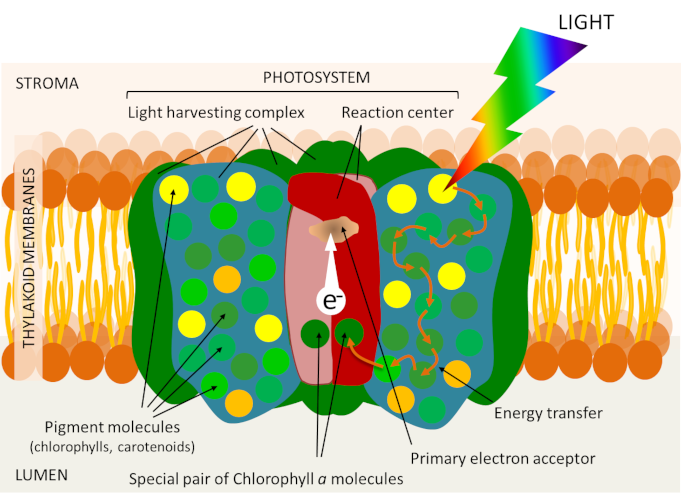
Shedding Light On Photosynthesis Encyclopedia Of The Environment Source: www.encyclopedie-environnement.org
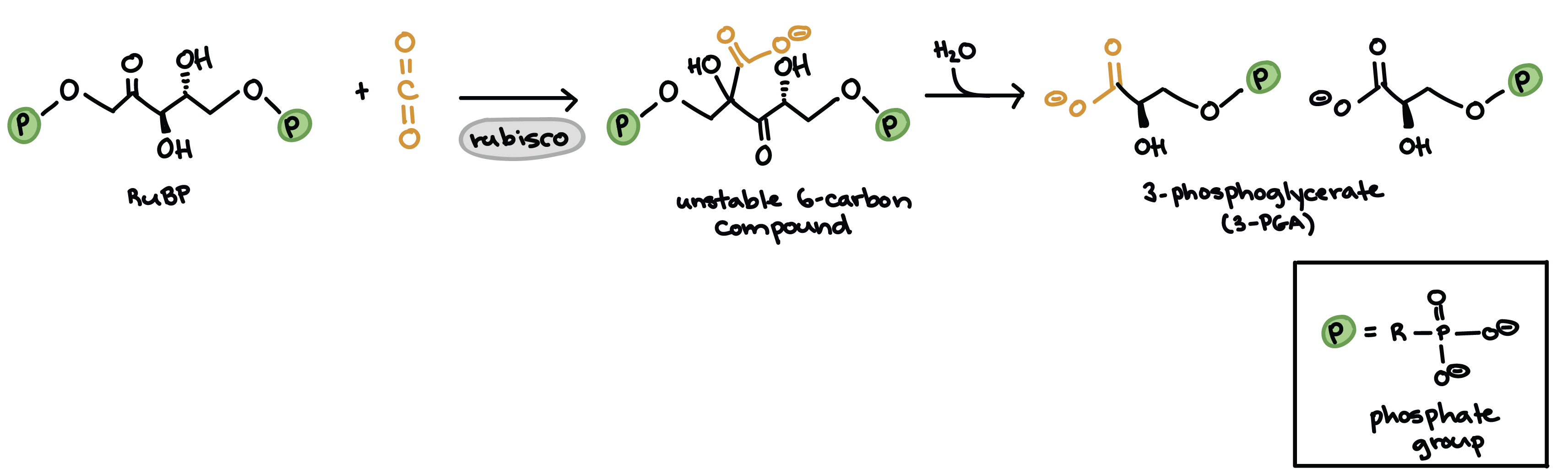
The Calvin Cycle Article Photosynthesis Khan Academy Source: www.khanacademy.org
